Naitbabies is a small Charitable Incorporated Organisation, registered in the UK and run by families who have been diagnosed with Foetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia – FNAIT

What is FNAIT
FNAIT is a life threatening bleeding disorder that results from incompatibility between mother and baby for platelet-specific antigens.
This may cause the maternal immune response to produce antibodies against platelet antigens that have been inherited paternally. Antibodies then destroy fetal platelets, leaving the fetus or neonate at risk of hemorrhaging into major organs such including the brain – ICH, stomach, spinal cord, kidneysand liver.
Babies are at serious risk of death or suffering lifelong disabilities.
Although well documented most people have never heard of FNAIT including, surprisingly, many obstetricians and midwives. Diagnosis is often not made until the second, third or even fourth pregnancy. The possibility of FNAIT being dismissed by clinicians as ‘too rare’ and bruising as ‘birth trauma’ or ‘ a newborn rash’.
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia affects 0.1% of births, with maternal antibodies crossing the placenta as early as 14 weeks’ gestation.
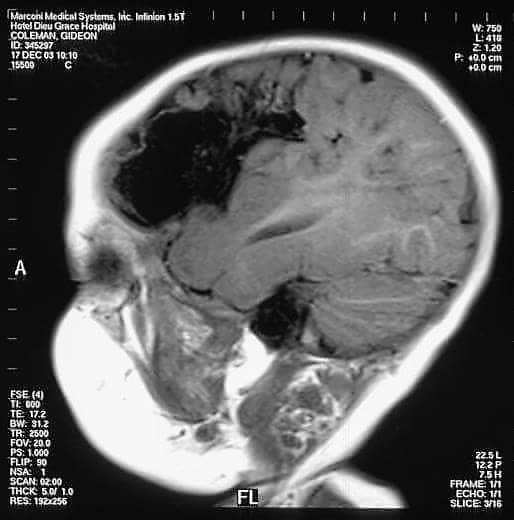
It is the most common cause of severely low platelets (thrombocytopenia) in an otherwise well neonate and may cause bleeding into major organs such as the stomach or spinal cord.
The most feared bleeding is into the baby’s brain – intracranial hemorrhage ICH.
Affecting approximately 1:1000 babies the true figure is unknown, due in part, to misdiagnosis and under-diagnosis.
Frequently thrombocytopenia is mild and the affected baby remains largely asymptomatic and therapeutic interventions are not indicated.
Baby’s with severe thrombocytopenia may exhibit hemorrhaging into major organs such as the spinal cord or stomach at, or a few hours after delivery. Intra-cranial hemorrhage may lead to death (10%) or long term disability (20%) which approximates to 63:100,000 babies.
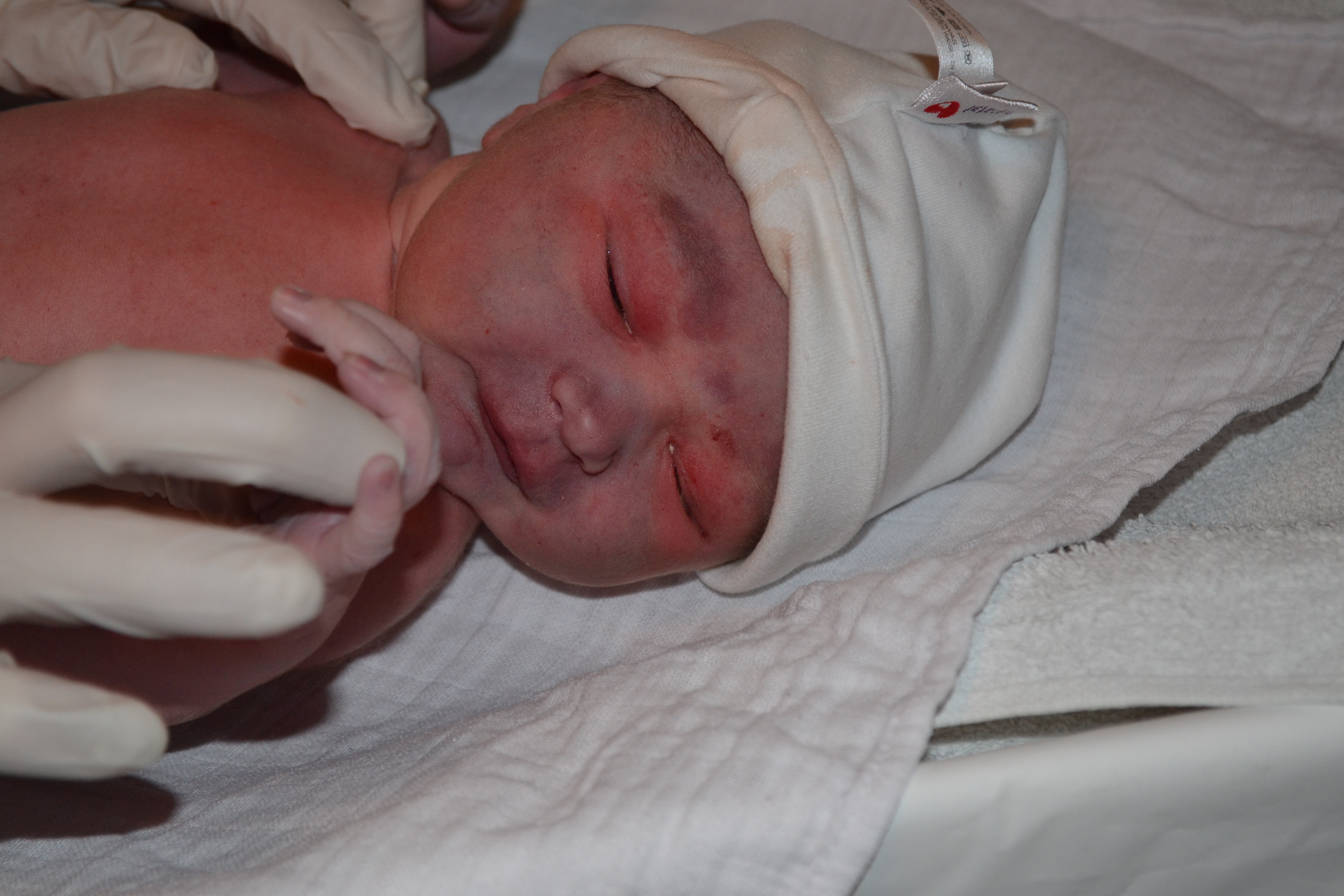
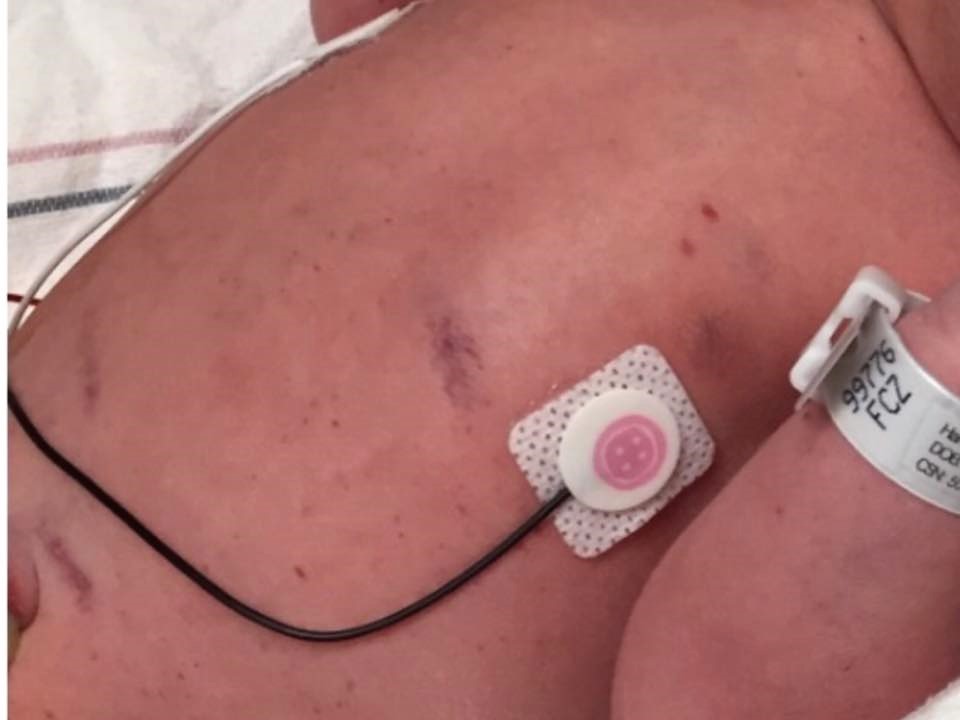
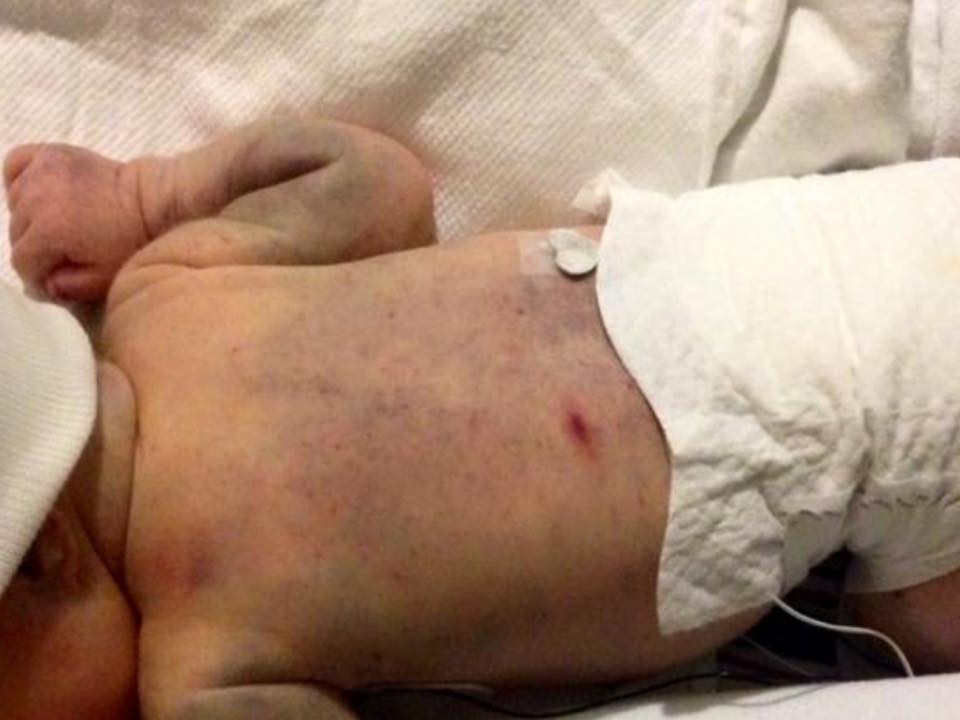
Signs of thrombocytopenia in a neonate are ICH, petechiae, ecchymosis, hydrocephalus, and bradycardia.
Milder visible signs (left) are not an indication of severity of platelet destruction and are often wrongly dismissed as bruising due to ‘birth trauma’.
There may be no external signs evident.
Neurological disabilities caused by brain hemorrhaging include hydrocephalus, cortical blindness, epilepsy, cerebral palsy, precocious puberty, sensory, motor and cognitive delays.
Recent research has indicated that miscarriage, inter uterine growth restriction (IUGR) and retinal damage is also associated with an FNAIT diagnosis.
Treatment for further pregnancies is available. If subsequent pregnancies are untreated there is a risk that future platelet counts may get progressively worse. Although stressful, weekly IVIG infusions (with or without corticosteroids) have an extremely high success rate.
FNAIT is the platelet equivalent of the red blood cell disease HDFN – Rhesus disease, which has been screened for since the late 1960’s. NO country screens for this condition although it is very well documented and has been since the 1950’s.
FNAIT is the platelet equivalent of the red blood cell disease HDFN – Rhesus disease, which has been screened for since the late 1960’s. NO country screens for this condition although it is very well documented and has been since the 1950’s.
Antenatal screening for FNAIT should be standard and routine - Much rarer diseases are screened for
Visit our Ebay shop.
Click on the link below, to view and buy from our Ebay shop.
Naitbabies are members of the following organisations








